Unlocking the Power of AIP Optimization: Why Asset Ranking Falls Short
Introduction
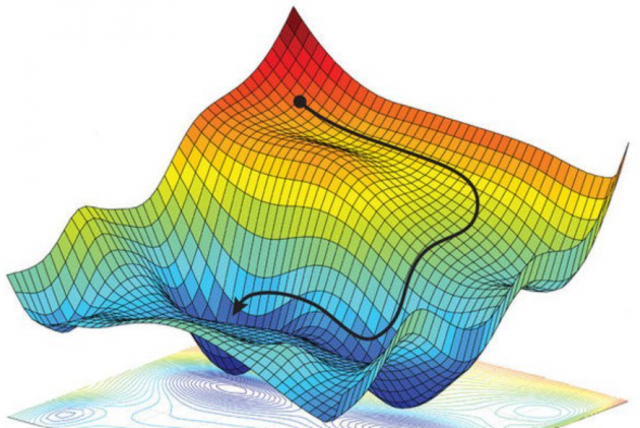
In the field of asset management, making informed decisions about resource allocation and prioritization is crucial. Traditionally, asset ranking methods have been employed to determine priority levels based on various criteria. However, these methods often fall short when it comes to accuracy and optimal resource allocation. In this blog post, we will explore why an asset ranking method is not as accurate as AIP optimization techniques and highlight the benefits of leveraging AIP optimization for improved decision-making.
- Limited Consideration of Interdependencies: Asset ranking methods typically focus on evaluating individual assets without considering the interdependencies between them. In reality, assets within a system are interconnected, and the performance of one asset can impact others. AIP optimization techniques, on the other hand, take into account the complex relationships and interdependencies among assets, enabling a holistic analysis that leads to more accurate decision-making.
- Inadequate Evaluation of Trade-offs: Asset ranking methods often fail to consider trade-offs between different assets or investment options. They provide a simplistic ranking based on isolated criteria, disregarding the potential synergies or conflicts that may arise. AIP optimization techniques, such as linear programming or simulation-based optimization, enable a comprehensive evaluation of trade-offs by considering multiple factors simultaneously. This approach allows for the identification of optimal investment strategies that maximize overall system performance and value.
- Lack of Risk Analysis: Asset ranking methods typically do not incorporate risk analysis, which is a critical aspect of asset management. Managing risks associated with asset failure, environmental impacts, regulatory compliance, and financial constraints is essential for effective decision-making. AIP optimization techniques provide the capability to assess risks and uncertainties through probabilistic modeling and optimization algorithms. This ensures that decisions are made with a clear understanding of potential risks and their impact on asset performance.
- Failure to Consider Long-Term Asset Performance: Asset ranking methods often focus on short-term considerations, such as immediate maintenance needs or criticality. While these factors are important, they do not provide a comprehensive view of long-term asset performance and value. AIP optimization techniques enable organizations to evaluate investment strategies over the asset lifecycle, considering factors such as deterioration models, life cycle costs, and performance targets. This long-term perspective ensures that decisions align with the organization's strategic objectives and optimize asset performance over time.
- Suboptimal Resource Allocation: Asset ranking methods can lead to suboptimal resource allocation as they rely on subjective criteria or simplified scoring systems. They may not consider budget constraints, resource availability, or the overall system-level impact of investment decisions. AIP optimization techniques, by contrast, provide a rigorous framework for allocating resources efficiently. They consider budgetary constraints, resource limitations, and desired levels of service to optimize investment decisions across multiple assets, maximizing the overall system performance within given constraints.
Conclusion
While asset ranking methods have traditionally been used for prioritization in asset management, they fall short in accuracy and optimal resource allocation. AIP optimization techniques offer a more sophisticated and comprehensive approach to decision-making. By considering interdependencies, evaluating trade-offs, incorporating risk analysis, focusing on long-term performance, and optimizing resource allocation, AIP optimization techniques empower organizations to make informed decisions that maximize asset performance and value. Embracing AIP optimization can improve asset management practices and help organizations achieve their strategic objectives more effectively.