The Role of GIS in Asset Investment Planning (AIP)
Introduction
Asset Investment Planning (AIP) is an essential process for organizations to manage their assets effectively and allocate investments strategically. One technology that has significantly enhanced AIP is Geographic Information System (GIS). GIS provides a powerful set of tools and capabilities to enhance decision-making by visualizing and analyzing asset data geographically. In this blog post, we will explore the role of GIS in AIP and how it helps organizations make informed investment decisions for their assets.
Data Visualization and Mapping
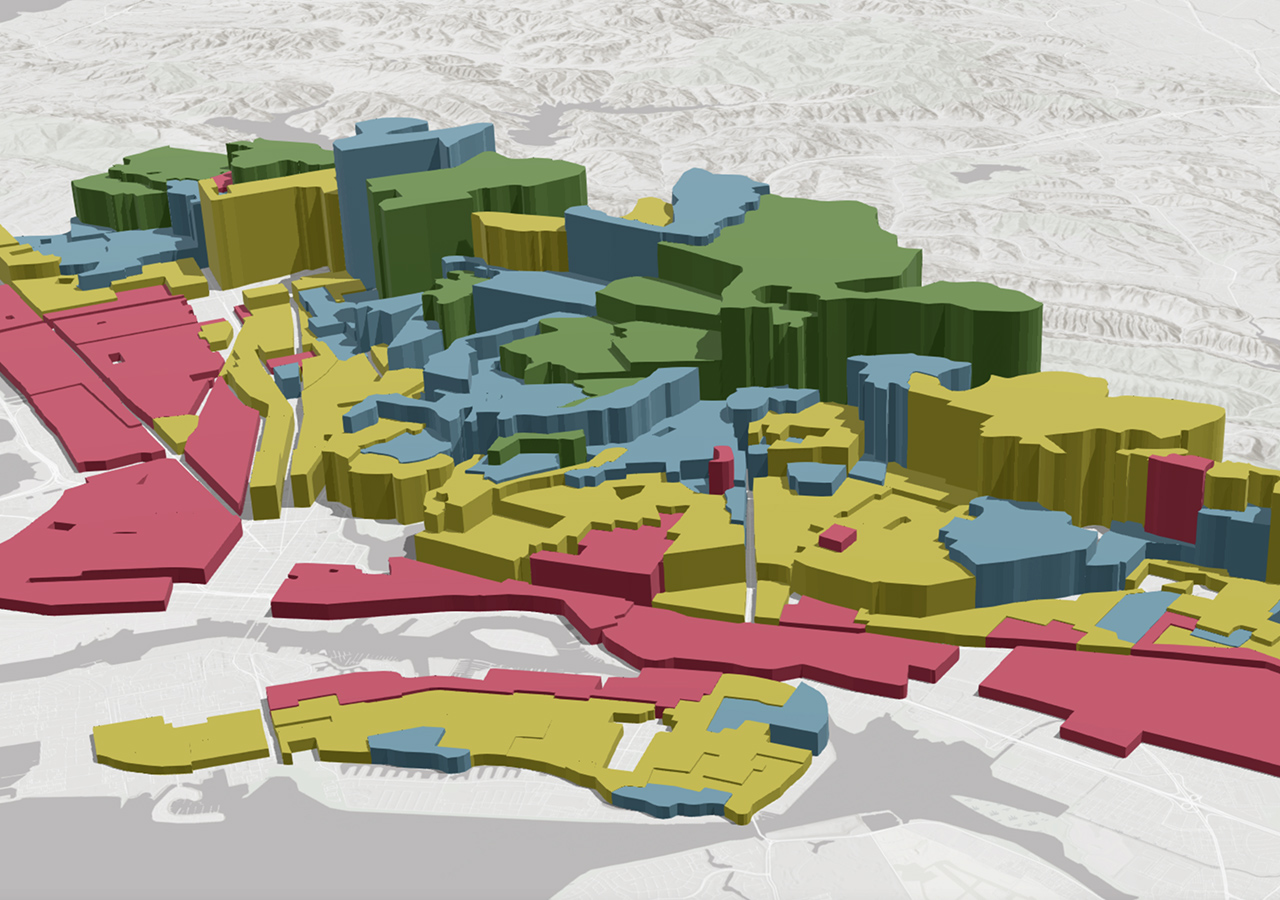
GIS allows organizations to visualize asset data on maps, providing a spatial context for asset management decisions. With GIS, asset managers can overlay various data layers, such as asset locations, condition assessments, maintenance history, and environmental factors. By visualizing assets on a map, organizations gain insights into spatial relationships, identify patterns, and understand the geographic distribution of assets. This helps in prioritizing investments based on asset criticality, service areas, and environmental factors.
Asset Inventory and Management
GIS enables organizations to create and maintain a comprehensive asset inventory. Asset managers can capture asset information, such as asset type, condition, age, and associated attributes, within the GIS database. By integrating asset data with spatial information, organizations can manage assets more effectively. GIS provides tools for querying and analyzing asset data, allowing asset managers to make informed decisions about asset maintenance, replacement, and investment planning. The ability to track assets in real-time on a map improves operational efficiency and helps optimize resource allocation.
Performance Analysis and Modeling
GIS supports performance analysis and modeling of assets. By integrating asset data with GIS, organizations can perform spatial analysis to understand the performance of assets in different geographic areas. GIS enables asset managers to identify asset hotspots, areas with high maintenance needs, and areas where investments are likely to yield the most significant returns. Moreover, GIS-based modeling tools can simulate different investment scenarios and predict the impact on asset performance. This allows organizations to optimize their investment strategies, prioritize projects, and allocate resources effectively.
Risk Assessment and Mitigation
GIS plays a crucial role in assessing and mitigating risks associated with assets. By overlaying asset data with environmental and hazard maps, organizations can identify assets at risk of natural disasters, climate change impacts, or other environmental factors. GIS-based risk assessment helps asset managers prioritize investments for mitigating risks and implementing preventive measures. By visualizing risks on a map, organizations can better understand the potential consequences of asset failures and make informed decisions to minimize risks and ensure the reliability and resilience of their assets.
Collaboration and Communication
GIS facilitates collaboration and communication among stakeholders involved in AIP. By providing a common platform for data sharing, asset managers, finance departments, and other decision-makers can access and analyze asset information collaboratively. GIS-based maps and visualizations simplify complex asset data and make it easier to communicate investment strategies and priorities to stakeholders. By sharing interactive maps and dashboards, organizations can engage stakeholders, foster transparency, and gather valuable insights for decision-making.
Conclusion
Geographic Information System (GIS) plays a crucial role in Asset Investment Planning (AIP). By leveraging GIS technology, organizations can harness the power of spatial data to visualize, analyze, and make informed decisions about their assets. GIS enhances data visualization, asset inventory management, performance analysis, risk assessment, and collaboration in AIP processes. By incorporating GIS into their asset management strategies, organizations can optimize investments, improve asset performance, and ensure the long-term sustainability of their assets.